Jupyter Notebooks
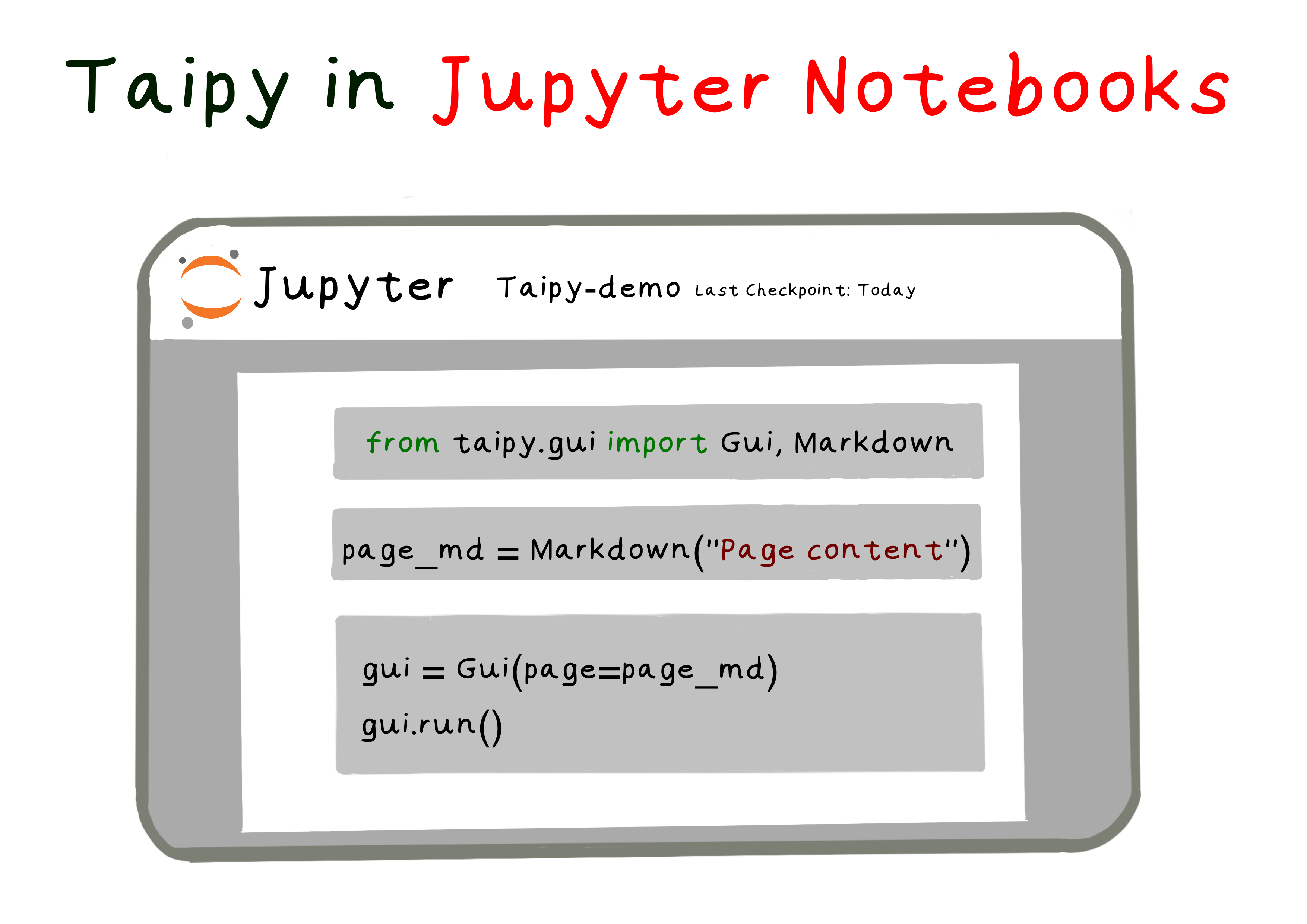
Taipy's built-in support for Jupyter Notebooks offers us:
-
Access to Taipy's complete set of data visualization and interactivity tools within our notebooks.
-
A safe environment for trying out Taipy's numerous features and functionalities.
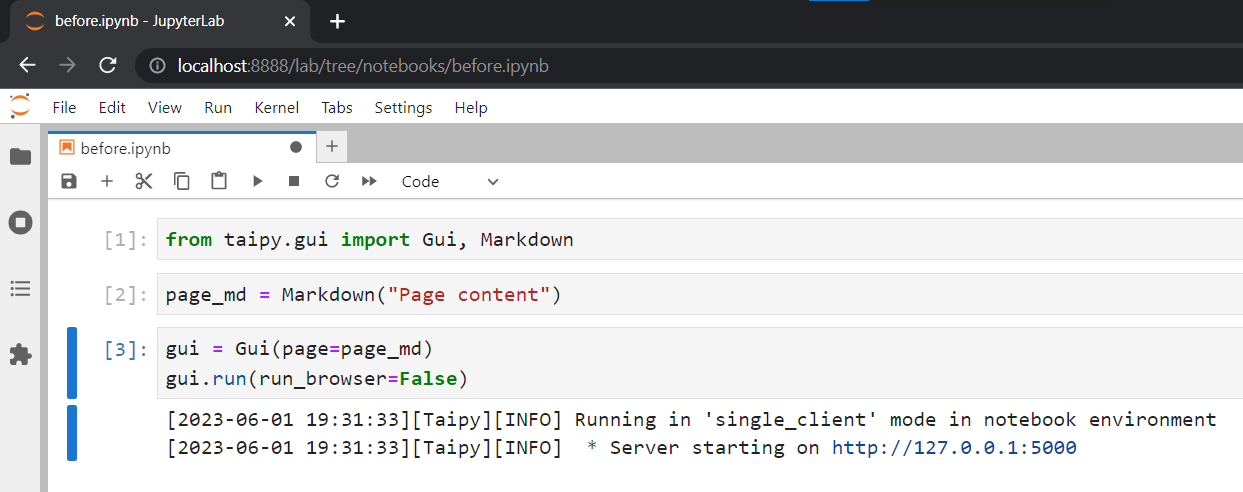
When using Taipy in Python scripts (.py), we typically have to rerun the script whenever we make changes to our code. In Jupyter Notebook (.ipynb), the equivalent would be to restart the kernel and rerun all cells, which can be cumbersome.
To solve this and enhance the experience of using Taipy in Jupyter Notebook, we should utilize two straightforward functions for updating the user interface after making changes to our code:
-
Page.set_content(): Use this method when you update the content of a page.
-
Gui.reload(): Use this method when you modify a variable that's used in a page.
Modifying Page Content¶
The code below illustrates how to create a basic Taipy web application in a Jupyter Notebook:

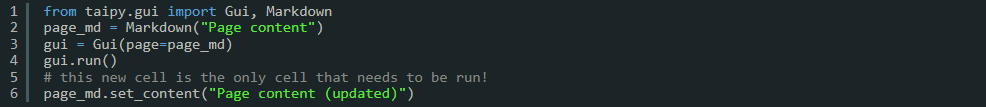
When we wish to alter the contents of page_md, we might be tempted to (incorrectly) modify and re-run our existing page definition cell, like this:

However, taking this approach will NOT produce the desired result on our webpage. Instead, we
should utilize the Page.set_content() method, such as page_md.set_content("New content"), like
this:
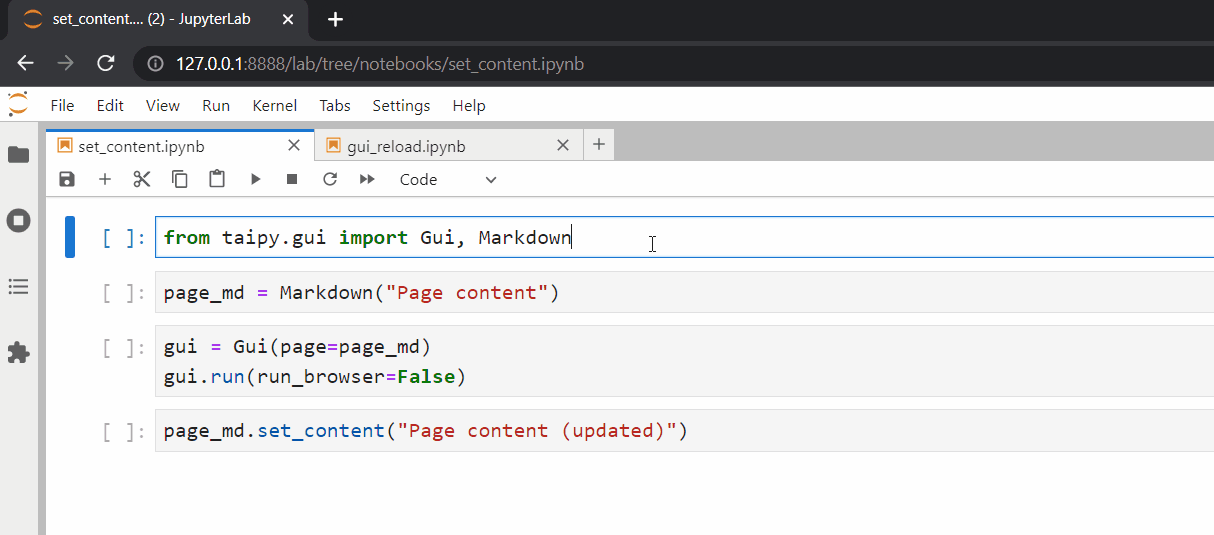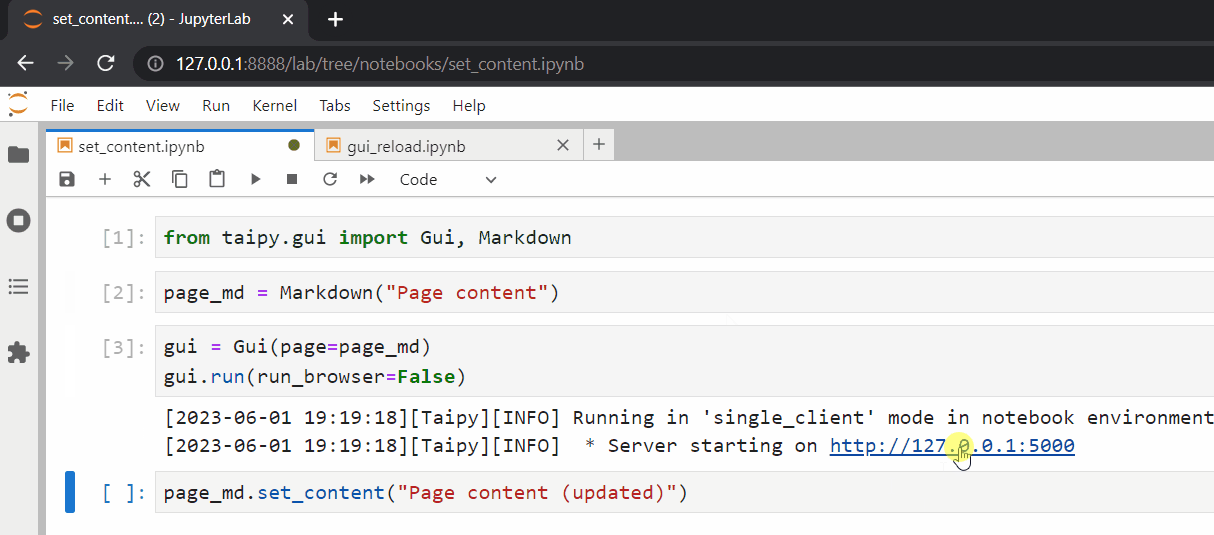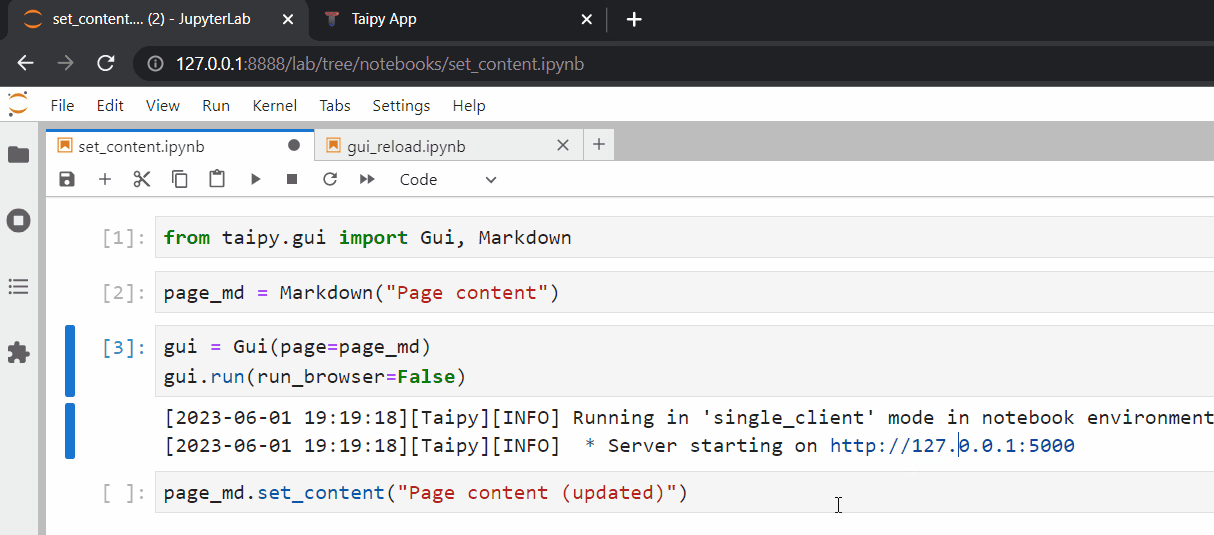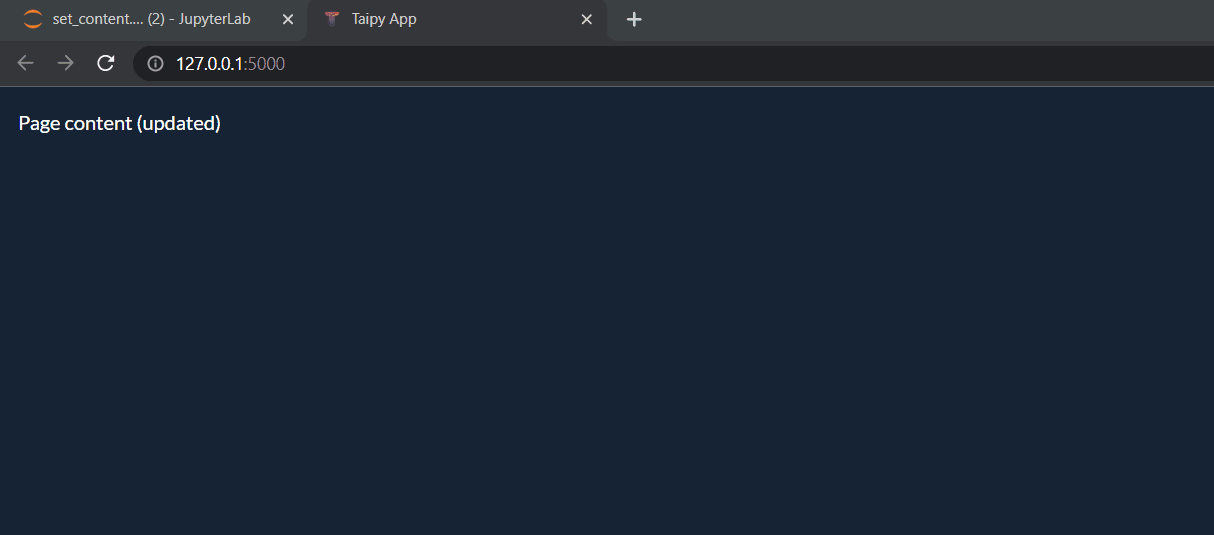
Simply running the new cell (and refreshing the browser) will correctly update our web page.
Modifying Variable¶
Another common task is to change the value of a variable used in our Page definition. Consider the following Jupyter Notebook as an example:
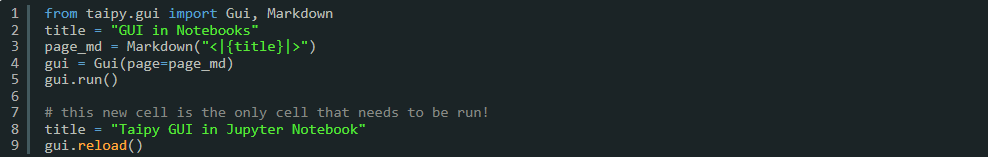
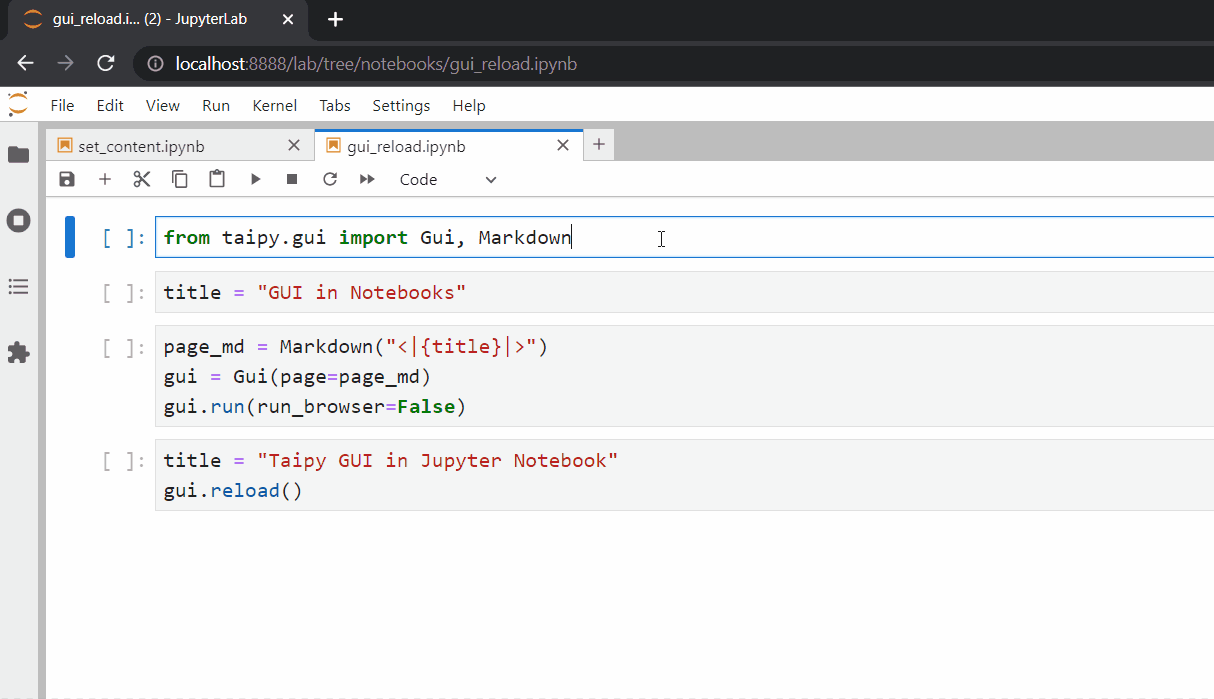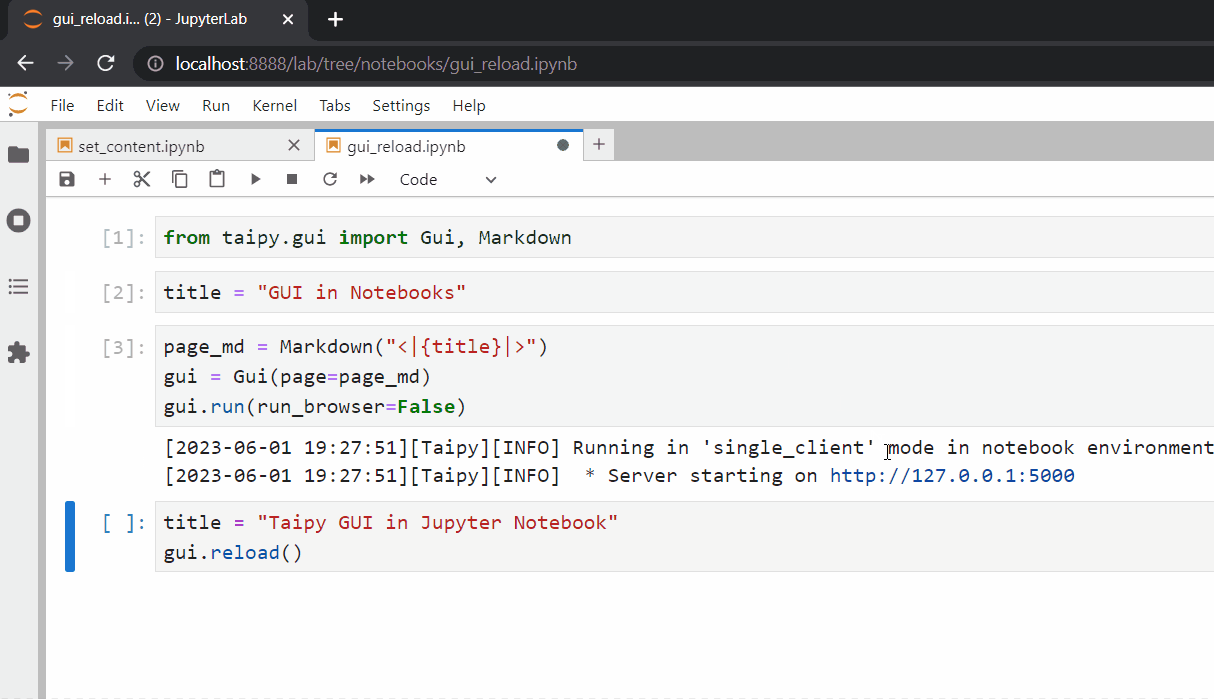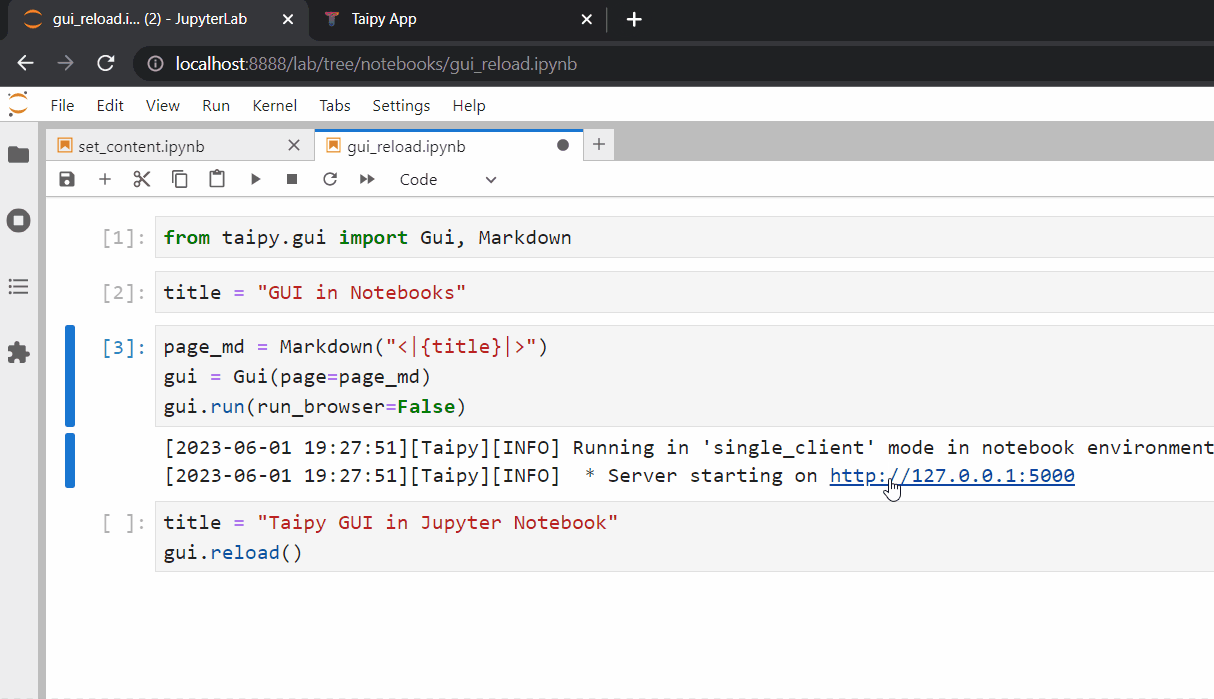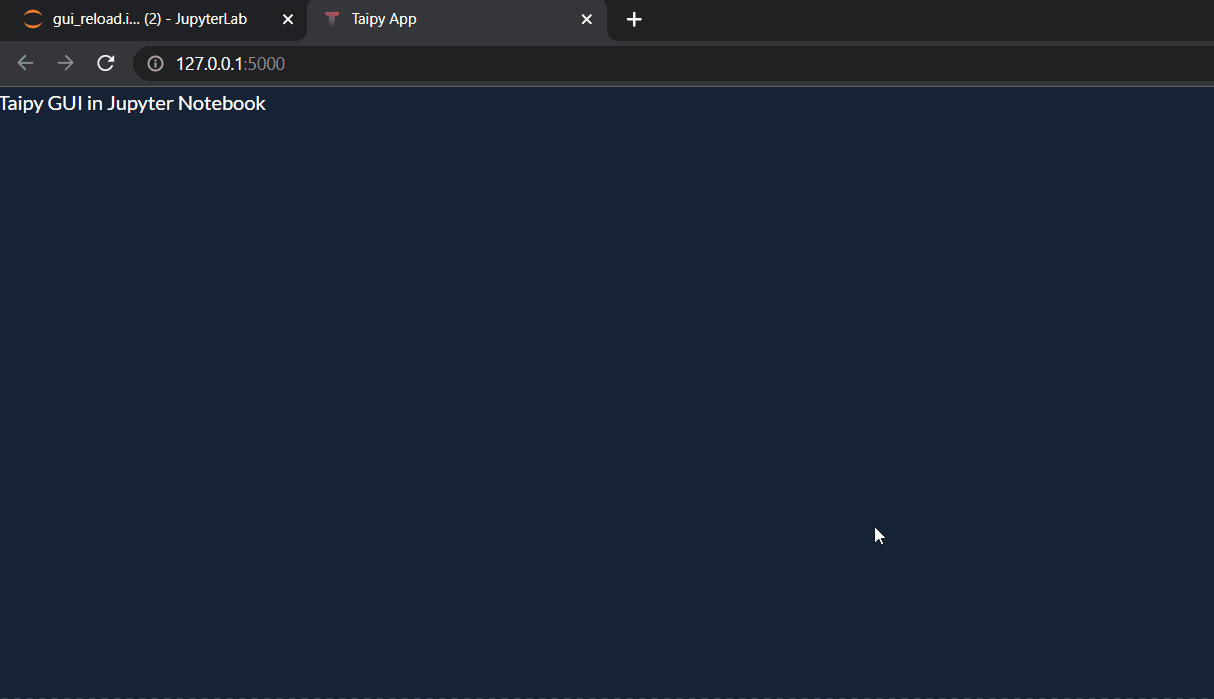
In this example, if we want to change the value of the title variable (e.g.,
title = "Taipy GUI in Jupyter Notebook"``), we need to inform Taipy of the changes by calling
theGui.reload()^method (e.g.,gui.reload()`).
This ensures that the most recent variable values are loaded from the Jupyter session namespace.
After running the cell, refresh your browser to view the updated changes.
This doesn't only relate to variables on pages, but also to
callback functions like on_change or user-defined callbacks.
Conclusion¶
Taipy is dedicated to offering complete web interfaces (GUIs) from both Python scripts and
notebooks.
To summarize, to effectively use Taipy's GUI in notebooks, remember to do the following:
-
Use
Page.set_content()after you make changes to a page's content. -
Utilize
Gui.reload()after you alter a variable that is used on a page.