3 - Scenario configuration
Scenario¶
Taipy provides an easy Scenario management to efficiently:
-
manage the execution of your functions/pipelines.
-
manage data sources and monitor KPIs.
It comes in handy in the context of Machine Learning or Mathematical optimization.
To apprehend what is a Scenario, you need to understand the Data node and Task concepts.
-
Data Nodes: are the translation of variables in Taipy. Data Nodes don't contain the data itself but point to the data and know how to retrieve it. These Data Nodes can point to different types of data sources like CSV files, Pickle files, databases, etc., and they can represent various types of Python variables such as integers, strings, data frames, lists, and more.
-
Tasks: are the translation of functions in Taipy where their inputs and outputs are data nodes.
-
Scenarios: Scenarios are created by combining Data Nodes and Tasks to form a graph that maps the execution flow. End-Users very often require modifying
various parameters to reflect different business situations. Taipy provide the framework to play/execute scenarios under different situations (i.e. various data/parameters values set by end-users).
Configuration Basics¶
Before creating and runnning our scenarios, we need to configure them properly.
Configuring Data Nodes¶
During Data Node configuration, the developer specifies the type or format of each Data Node, along with its scope.
-
Storage Type: Specifies the storage type for the Data Node, e.g., CSV file, Pickle file, etc. The initial dataset, for example, is a CSV file with storage_type="csv".
-
Scope: Defines the scope of the Data Node. There are three types of scope in the code: Global, Cycle, and Scenario scope.
1- Scope.SCENARIO (default): Having one data node for each scenario.
2- Scope.CYCLE: Extend the scope by sharing data nodes across all scenarios of a given cycle.
3- Scope.GLOBAL: Finally, extend the scope globally (across all scenarios of all cycles). For example, the initial/historical dataset is usually shared by all the scenarios/cycles. It is unique in the entire application.
In a Machine Learning context, it's typical to have multiple training and testing models. In this tutorial, we set up a scenario where we predict the values for the upcoming days based on a specific day, using two models: a baseline model and a Machine Learning model.
-
Retrieval of the initial dataset,
-
Data Cleaning,
-
Predictions (for number of predictions) from day onwards. In our example, predictions represents the number of items sold in a given store on a 15-min basis.
-
Creation of metrics and of a dataset for visualization.
The graph below represents the scenario to configure, where tasks are in orange and data nodes in blue.
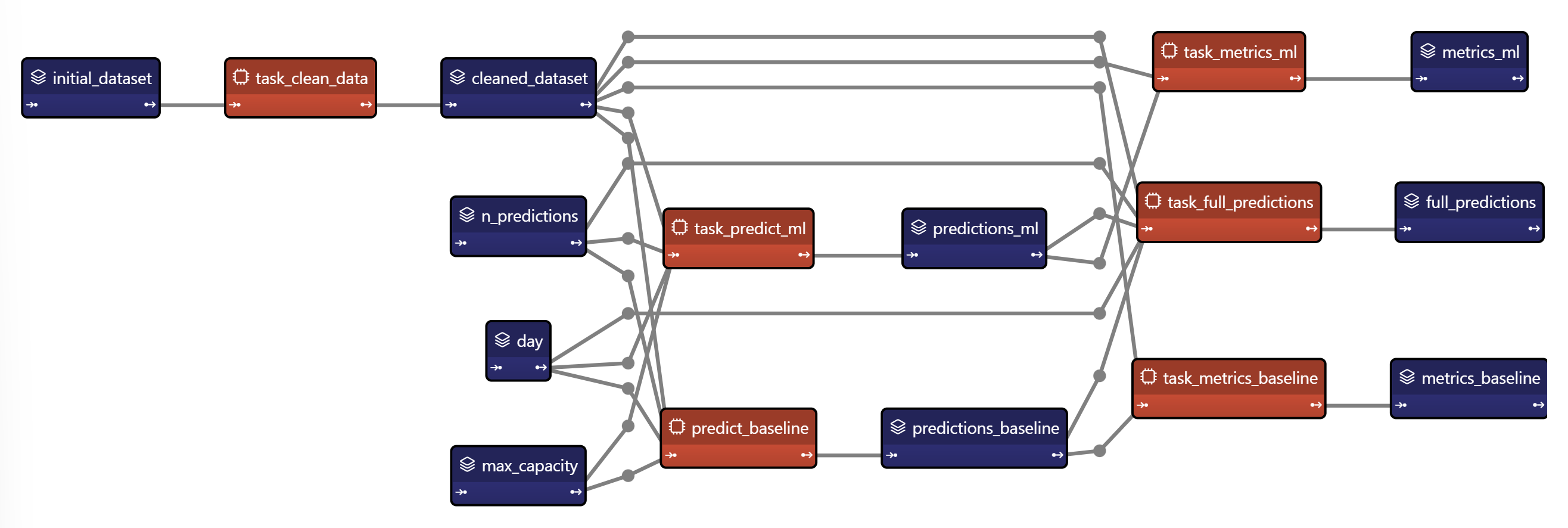
Input Data Nodes Configuration¶
These are the input Data Nodes. They stand for the variables/data sources in Taipy when a scenario is run. However, initially, we need to set them up to build the DAG.
-
initial_dataset is simply the initial CSV file. Taipy needs some parameters to read this data: path and header. The
scopeis global; each scenario has the same initial dataset. -
day is the beginning of the predictions. The default value is the 26th of July. It means the training data will end before the 26th of July, and predictions will begin on this day.
-
n_predictions is the number of predictions you want to make while predicting. The default value is 40. A prediction represents the number of items sold in a given store per 15-minute time slot.
-
max_capacity is the maximum value that can take a prediction; it is the ceiling of the projections. The default value is 200. It means that, in our example, the maximum number of items sold per 15 minutes is 200.
import datetime as dt
import pandas as pd
from taipy import Config, Scope
## Input Data Nodes
initial_dataset_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="initial_dataset",
storage_type="csv",
path=path_to_csv,
scope=Scope.GLOBAL)
# We assume the current day is the 26th of July 2021.
# This day can be changed to simulate multiple executions of scenarios on different days
day_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="day", default_data=dt.datetime(2021, 7, 26))
n_predictions_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="n_predictions", default_data=40)
max_capacity_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="max_capacity", default_data=200)
Intermediate and output Data Nodes¶
-
cleaned_dataset is the dataset after cleaning (after the
clean_datafunction). -
predictions_ml and predictions_baseline are the predictions of the model. They are the output of
predict_baseline()andpredict_ml()functions. -
full_dataset is the concatenation of the predictions.
-
The metrics Data Nodes store KPIs about the predictions.
## Remaining Data Nodes
cleaned_dataset_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="cleaned_dataset",
scope=Scope.GLOBAL)
predictions_baseline_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="predictions_baseline")
predictions_ml_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="predictions_ml")
full_predictions_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="full_predictions")
metrics_baseline_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="metrics_baseline")
metrics_ml_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="metrics_ml")
Configuring Tasks¶
Tasks are the translation of functions in Taipy. Each task has an ID, a function, inputs, and outputs.
clean_data task¶
The first task that you want to create is your clean_data task.
It will take your initial dataset (input Data Node),
clean it (calling the clean_data function) and generate the cleaned dataset Data Node.
This task will only execute once thanks to the skippability feature of Taipy.
clean_data_task_cfg = Config.configure_task(id="clean_data",
function=clean_data,
input=initial_dataset_cfg,
output=cleaned_dataset_cfg,
skippable=True)
predict_baseline task¶
This task will use the cleaned dataset and make predictions based on your specified parameters, which are the three input Data Nodes:
Day, Number of predictions and Max Capacity.
predict_baseline_task_cfg = Config.configure_task(id="predict_baseline",
function=predict_baseline,
input=[cleaned_dataset_cfg, n_predictions_cfg, day_cfg, max_capacity_cfg],
output=predictions_cfg)
The other tasks (predict_ml, metrics_baseline, metrics_ml, and full_prediction) are
being configured the same way to get the metrics from the two models and a dataset
with all the predictions and historical data.
Scenario Configuration¶
All the task and Data Node configurations can create a scenario. These tasks that form an execution graph will be executed when a scenario is submitted.
scenario_cfg = Config.configure_scenario(id="scenario",
task_configs=[clean_data_task_cfg,
predict_baseline_task_cfg,
predict_ml_task_cfg,
metrics_baseline_task_cfg,
metrics_ml_task_cfg,
full_predictions_task_cfg],
frequency=Frequency.WEEKLY)
Entire code¶
The following Python code corresponds to the configuration/config.py file.
import datetime as dt
import pandas as pd
from taipy import Config, Scope, Frequency
from algos.algos import *
path_to_csv = "data/dataset.csv"
# Datanodes
## Input Data Nodes
initial_dataset_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="initial_dataset",
storage_type="csv",
path=path_to_csv,
scope=Scope.GLOBAL)
# We assume the current day is the 26th of July 2021.
# This day can be changed to simulate multiple executions of scenarios on different days
day_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="day", default_data=dt.datetime(2021, 7, 26))
n_predictions_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="n_predictions", default_data=40)
max_capacity_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="max_capacity", default_data=200)
## Remaining Data Nodes
cleaned_dataset_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="cleaned_dataset",
scope=Scope.GLOBAL)
predictions_baseline_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="predictions_baseline")
predictions_ml_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="predictions_ml")
full_predictions_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="full_predictions")
metrics_baseline_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="metrics_baseline")
metrics_ml_cfg = Config.configure_data_node(id="metrics_ml")
# Tasks
clean_data_task_cfg = Config.configure_task(id="task_clean_data",
function=clean_data,
input=initial_dataset_cfg,
output=cleaned_dataset_cfg,
skippable=True)
predict_baseline_task_cfg = Config.configure_task(id="predict_baseline",
function=predict_baseline,
input=[cleaned_dataset_cfg, n_predictions_cfg, day_cfg,
max_capacity_cfg],
output=predictions_baseline_cfg)
predict_ml_task_cfg = Config.configure_task(id="task_predict_ml",
function=predict_ml,
input=[cleaned_dataset_cfg,
n_predictions_cfg, day_cfg,
max_capacity_cfg],
output=predictions_ml_cfg)
metrics_baseline_task_cfg = Config.configure_task(id="task_metrics_baseline",
function=compute_metrics,
input=[cleaned_dataset_cfg,
predictions_baseline_cfg],
output=metrics_baseline_cfg)
metrics_ml_task_cfg = Config.configure_task(id="task_metrics_ml",
function=compute_metrics,
input=[cleaned_dataset_cfg,
predictions_ml_cfg],
output=metrics_ml_cfg)
full_predictions_task_cfg = Config.configure_task(id="task_full_predictions",
function=create_predictions_dataset,
input=[predictions_baseline_cfg,
predictions_ml_cfg,
day_cfg,
n_predictions_cfg,
cleaned_dataset_cfg],
output=full_predictions_cfg)
# Configure our scenario which is our business problem.
scenario_cfg = Config.configure_scenario(id="scenario",
task_configs=[clean_data_task_cfg,
predict_baseline_task_cfg,
predict_ml_task_cfg,
metrics_baseline_task_cfg,
metrics_ml_task_cfg,
full_predictions_task_cfg],
frequency=Frequency.WEEKLY)

